Case metadata
Mercury is a repository of metadata about objects along with definitions of GUI controls enabling the generation of GUI forms. Metadata is structured information used to describe objects (cases) - it describes the logical and physical relationship between parts of a complex object (see Describing digital objects, October 21, 2016 [accessed 2020-07-01]). Mercury DB in its structures also allows for storing the necessary data allowing for the generation of edit forms and presentation pages of stored objects. Metadata is stored in a relational database (SQL). A synonym for the definition of case metadata is the case type. Below is a description of the entity.
TypeCase
| Layers used | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | TypeCase |
An entity representing a case type. An object used in the logical layer services. Below is a diagram of TypeCase relationships with other entities described in this document.
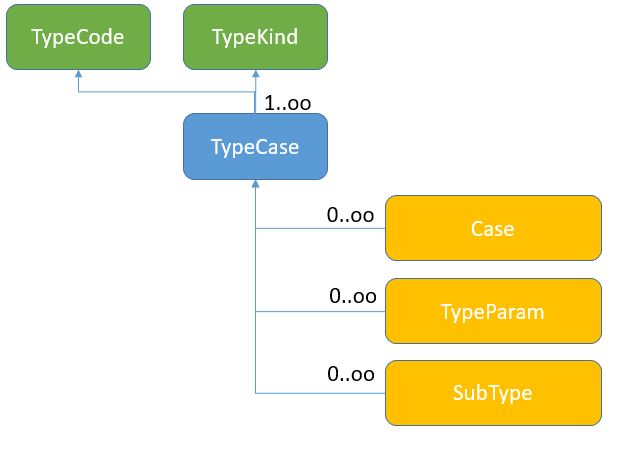
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Type identifier. Unique value within the repository. | Long | Yes | |
| accountNumber | Default accounting account code assigned to a given type. This data is the basis for generating a unique inventory number. | String | No | |
| checkStoreCounter | Whether to check the counter counting the number of documents of a given type. Counting via triggers in case object modification mechanisms. | Boolean | No | Default value false |
| code | Type code – a simple name grouping all versions of the type | TypeCode | Yes | |
| description | Description of the type version | String | No | |
| fromDate | Validity of the type version – date from. Parameter used to narrow down search results (to a set of cases in types occurring in a given time period) | Calendar | No | |
| isActive | Is the type active? | Boolean | No | Default value true |
| isDocumentType | Is the given type a document type? In connection with the CMIS Electronic Document Archive, information whether the type is a document type. | Boolean | No | |
| isEditable | Is the type modifiable?. Document types are not modifiable, because they will be synchronized with the AE (Electronic Archive, a document repository in the CMIS standard). Issue types, on the other hand, can be subject to changes introduced by the user. | Boolean | No | Default value true |
| isLatestVersion | Is this the currently valid version of the given type. | Boolean | No | |
| kind | Type group identifier | TypeKind | Yes | |
| sourceOfObject | Names of data sources of the type definition origin. | List<String> | No | Data can be passed via the context object. |
| subTypes | List of complex types associated with appropriate parameters | Set<SubType> | No | |
| sumControl | Checksum calculated based on the names of the definitions of all parameters - it is one of the bases for identifying the same types. | String | No | |
| toDate | Type version validity - date to. Parameter used to narrow down search results (to a set of issues in types occurring in a given time period) | Calendar | No | |
| typeName | Type name | String | Yes | |
| typeParams | List of type parameters | List<TypeParam> | Yes | |
| version | Type version number | Long | No |
TypeParam
| Layers used | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | TypeParam |
An object representing a type parameter. An object used in the services of the logical layer. Below is a diagram of the relationships between the TypeParam object and other entities described in this document.
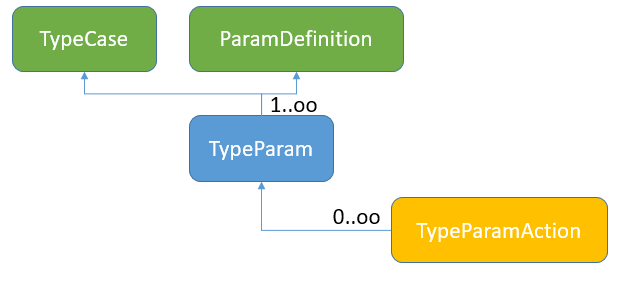
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | The type parameter identifier. A unique value within the repository. | TypeParamPK | Yes | |
| paramDefinition | Parameter identifier | ParamDefinition | Yes | |
| label | Label of the field appearing on the GUI form | String | No | |
| tooltip | User action tooltip associated with the field on the GUI form | String | No | |
| updateable | Can the field be edited/changed using the GUI form | String | No | Default value true |
| withEmptyOption | Can a GUI form field contain an empty option? | Boolean | No | |
| isRequired | Is it mandatory or is it required to fill in the value? Control field for form generation mechanisms. | Boolean | No | Default value false |
| isSearchData | Is it available in search? | Boolean | No | Default value true |
| hasMultiValues | Can we insert multiple values into a field, regardless of whether we are dealing with a regular simple field, e.g. INTEGER or a multilist. | Boolean | No | Default value false |
| arg1 | Universal argument no. 1. Control field for GUI form generation mechanisms. | String | No | |
| arg2 | Universal argument no. 2. Control field for GUI form generation mechanisms. | String | No | |
| arg3 | Universal argument no. 3. Control field for GUI form generation mechanisms. | String | No | |
| arg4 | Universal argument no. 4. Control field for GUI form generation mechanisms. | String | No | |
| arg5 | Universal argument no. 5. Control field for GUI form generation mechanisms. | String | No | |
| xmlId | XML identifier - a field added to XML needed to identify fields with the same names but different labels | String | Yes | |
| actions | List of Javascript actions assigned to the field on the GUI form. Control field for form generation mechanisms | Set<TypeParamAction> | No |
TypeParamPK
| Layers used | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | TypeParamPK |
Primary key of the TypeParam entity (type parameter) binding the type identifier and the position where the parameter occurs.
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | Case type identifier (reference to TypeCase entity). | TypeCase | Yes | |
| position | Field number to which the parameter is related, default position on the GUI form in vertical configuration. | Integer | Yes | Numeric field with values from 1 to 128 (maximum number of parameters). |
Control fields and their value definitions for GUI presentation generation mechanisms
Below, fields whose control meaning is not apparent from the description in the table with the object description will be listed. Some generation actions are supplementary to control fields defined in the associated ParamDefinition entity.
isRequired
Control field for form generation mechanisms. The value true means that the field is required. The value false means that the field is not required. If the ParamDefinition indicates that the field represents a SELECT control (HTML tag <select> ) or MULTI (HTML tag <select multiple>) on a GUI form, and the field value is false, the option list will be expanded with an empty value of --- select ---.
arg1
The field represents universal argument no. 1. Depending on what data is contained in ParamDefinition, the field obtains different control meanings:
- For
SELECTorMULTIcontrols, this is information whether the value or name should be extracted from the option element. The valuetruemeans getting thevalueattribute. - For a control representing TEXTAREA, this is the number of columns (characters in the horizontal direction).
- For a control representing a simple input, this is its type:
textorpassword - For a control representing an entered date, this is the JavaScript date format, e.g.
yyyy MM dd - For a control representing an entered number, this is the number format.
- For a control representing a file, this is the value representing the type of the loaded file. Possible values are
[img|doc|xls|pdf|unknown]
arg2
The field represents universal argument no. 2. Depending on what data is contained in ParamDefinition, the field obtains different control meaning:
- For
SELECTorMULTIcontrols, this is information representing thesizeattribute. - For a control representing TEXTAREA, this is the number of lines (characters vertically).
- For a control representing simple input, this is the size of this field.
- For a control representing an entered date, this is the position of the calendar icon (value
left– on the left side of the form field,right– on the right side) - For a control representing a file, this is the size of the field
arg3
The field represents universal argument no. 3. Depending on what data is contained in ParamDefinition, the field obtains a different control meaning:
- For SELECT or MULTI controls, this is information whether the concatenation of value and name (
value{separator}name, where the value{separator}defaults to the value of the stick character|) should be extracted from the list, the valuetruemeans that yes. - For a control representing a simple input, this is the maximum number of characters.
arg4
The field represents universal argument no. 4. Depending on what data is included in the ParamDefinition, the field obtains different control meanings:
- For controls representing LOB type data, these are data concerning metadata describing this object (used to present the object preview):
JSON,ANY,FILE,XML,HTML,TEXT.
arg5
The field represents universal argument no. 5. Depending on what data is included in the ParamDefinition, the field obtains different control meanings:
- For controls representing LOB type data, these are the object's mimeType data (used to present the object preview):
public String getDefaultContentType() {
switch (this) {
case JSON:
return "application/json";
case XML:
return "application/xml";
case HTML:
return "text/html";
case FILE:
return "application/octet-stream";
default:
return "text/plain";
}
}
actions
A list of JavaScript actions/functions assigned to a field on a GUI form. See the description of the TypeParamAction entity.
TypeCode
| Layers used in | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | TypeCode |
Code that groups different versions of the same type.
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | Identifier, name of the type code. | String | Yes | |
| alias | For presentation on forms or to show that a type is derived from another type - most useful for codes describing packages. | String | No | |
| color | Background color. For presentation on forms or lists: color presented in RGB hexadecimal | String | No | HTML color in RGB hexadecimal, e.g. ffdecc |
| fgcolor | Text color. For presentation on forms or lists: color presented in RGB hexadecimal | String | No | HTML color in RGB hexadecimal, e.g. 010101 |
| icoSrc | Logo/icon representing the given issue type. For presentation on forms or lists: HTML source (for SRC tag). Can be presented as URL or appropriate base64 | String | No | Indication of http source. |
| label | Label representing the given issue type. For presentation on forms. Can be empty. | String | No | |
| publishVersion | The version is changed with each update - needed to identify whether a given entry has already been published. | String | No | Generated value |
| uniqueConstraintParamName | Field name that contains unique values within a given type | String | No | Field name that appears in the set of parameters for the representation of the case type. |
| retentionTimeMilis | Time, expressed in milliseconds, after which the case object of a given type will be deleted, counted from the time/date of its creation. | Long | No | |
| useArchivization | Flag indicating whether the case archiving method should be used when deleting a case of a given type. | Boolean | No | true or false |
| subjectFormula | Formula for building the subject of a case of a given type. This formula is a definition of the concatenation of field names of a given type. | String | No | |
| partitionName | The name of the root partition of the Case entity, where case data of a given type is stored. | String | No |
Control fields and their value definitions for GUI presentation generation mechanisms
The TypeCode entity contains control fields that can be used to create GUI presentation mechanisms.
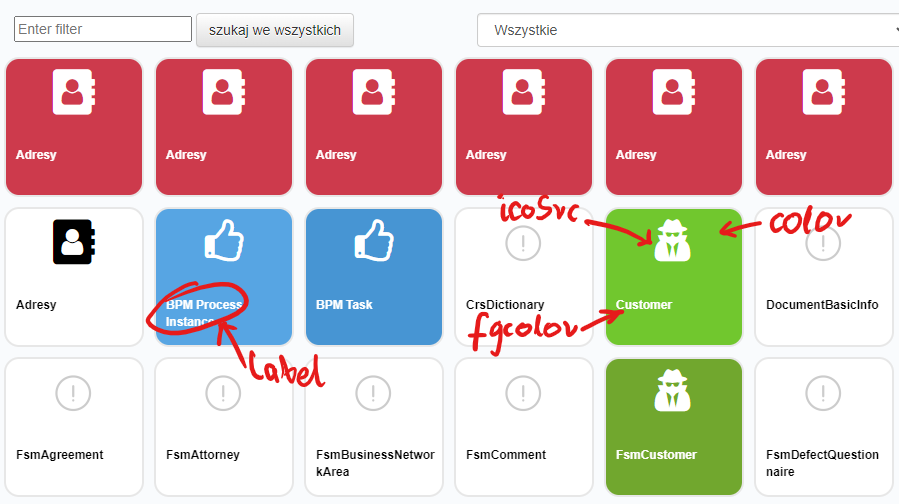
The above illustration shows how issue types can be presented in a presentation layer application. It also shows how the values of the color, fgcolor, icoSrc and label fields can be used when building a GUI.
Field icoSrc
A logo/icon representing a given issue type used for presentation on forms. The GUI implementation, which was presented in the previous illustration, uses iconography from the Font Awesome version 4 collection. The field accepts sample values: fa-thumbs-o-up, fa-bars, fa-address-book, fa-gavel, fa-user-secret etc. On the GUI side, the field value is retrieved to generate the following code:
<html>
<head>
<link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="/mercury-gui-portal/static/css/font-awesome.min.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<i class="fa fa-thumbs-o-up fa-3x" aria-hidden="true"></i>
</body>
</html>
Field subjectFormula
Formula for building a value representing the subject of a case of a given type. This formula is a definition of concatenation of fields of a given type and literal values. The formula is used to present the value of the subject field of the CaseNarrative object, which is an element used in the presentation of search results in the GUI presentation layer.
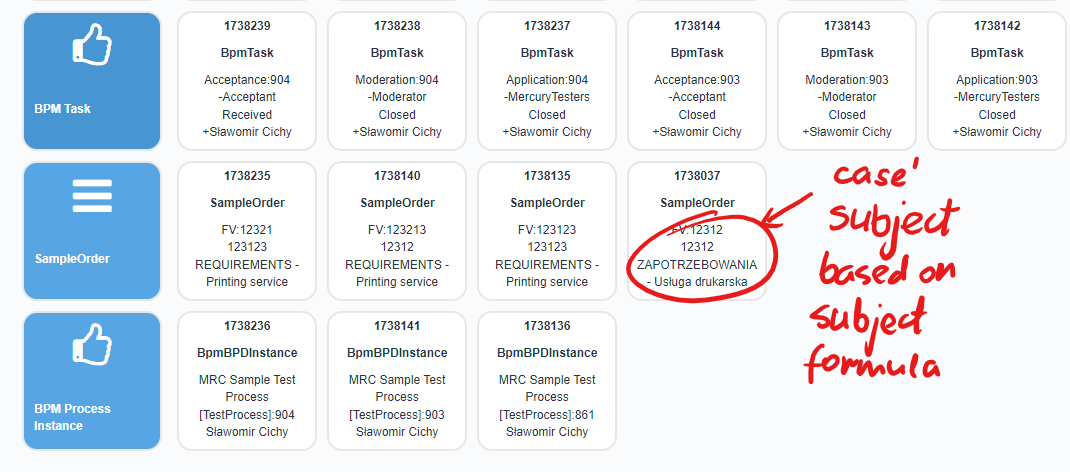
Below are examples of values that the field can take to present teasers1 of cases:
activityName||':'||bpmProcessInstanceId||'<br/>'||bpmGroupDisplayName||'<br/>'||bpmTaskStatus||'<br/>'||userFullName
city||' '||street
county||' '||community||' '||city||' '||street||' '||buildingNumber
'FV:'||invoceNo||'<br/>'||documentNo||' '||category
TypeKind
| Layers used | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | TypeKind |
Kind of type / category of type.
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | The identifier, name of the type type. | String | Yes | |
| description | A description of the type. | String | No |
Examples of types:
INW- InventoryASSETS- Fixed assetsGEN- Generated type definitions
SubType
| Layers used | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | SubType |
Data about the dependent case type and the dependent case form position on the main form (parent case).
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Subtype identifier. Unique value within the repository. | Long | Yes | |
| parentType | Case type identifier | TypeCase | Yes | |
| code | Type code | TypeCode | Yes | |
| isSearchData | Available in search? | Boolean | No | true or false |
| label | Header of dependent case form presentation. | String | No | |
| isList | Are dependent cases presented as a list? | Boolean | No | true or false |
| fieldName | Name of the parent case field to which the given dependent case form is associated. | String | No | |
| tooltip | User action tooltip associated with a field on the GUI form | String | No | |
| updateable | Is the dependent case form (data) changeable? | String | No | true or false |
TypeParamAction
| Layers used | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | TypeParamAction |
A collection of actions along with JavaScript code that are associated with GUI form fields.
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Action identifier. Unique value within the repository. | Long | Yes | |
| typeParam | Pointer to type parameter | TypeParam | Yes | |
| jsEventName | The name of the JavaScript event associated with the field of the given type. | String | Yes | HTML event names2 |
| jsFunctionBody | JavaScript code implementing the function. | LOB | Yes |
ParamDefinition
| Layers used | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | ParamDefinition |
An entity representing basic information about the name of a field, its simple or complex type. ParamDefinition is an element that is used repeatedly as a definition of a case type parameter, and can appear in many different types. It is a definition of a case type parameter. For example, a field named name can be used in many different types defining a user object, car, plane, computer.
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Parameter definition identifier. Unique value within the repository. Composite key. | ParamDefinitionPK | Yes | |
| description | Parameter description | String | No | |
| alternateName | Alternative name of the parameter. | String | No | |
| recommendedLabel | Recommended label describing the given definition. | String | No | |
| isLatestVersion | Is this the latest version of the field definition? | Boolean | Yes | true or false |
| isIndexable | Is the field indexed in the Lucene index, or is it possible to search for this field using Lucene mechanisms. | Boolean | No | true or false |
| htmlControlName | Name of the HTML control type, a field on a GUI form. | String | Yes | Values representing the HtmlSupportedControl object described later in the document. |
| paramType | Parameter type, value | String | Yes | Values representing the AttributeType object described later in the document. |
| subType | Information for complex types and what type the element is. | String | No | Name of the case type (TypeCase object) representing the dependent case assigned to the field. |
| timeToLiveSeconds | The parameter is optionally defined and defines the expiration time of the attribute cache. | Long | No | Numeric value |
| valueDefinition | Optional definition of the parameter value (when dealing with dictionary values). | String | No | |
| sourceType | Optional field for dictionary types - information about what type the value definition is. | String | No | Value representing the SourceType object described later in the document. |
| source | The name/definition of the source from which the dictionary data for the select fields comes. | String | No | |
| sourceJndiName | The general JNDI name of the source with exceptions. | String | No | |
| sourceJ2CName | Name indicating the identity and password of users used by the Java(TM) 2 Connector technology link security architecture. | String | No | |
| presentationUrlPrefix | URL prefix (HTTP, HTTPS paths) that is generated during value presentation (the field value is appended to the end of the URL). | String | No | |
| complexClass | The name of the Java class that represents the complex object stored in the given field. | String | No | |
| defaultValue | The default value of the parameter field | String | No | |
| fromDate | Type version validity – date from. Parameter used to narrow down search results (to a set of issues in types occurring in a given time period) | Calendar | No | |
| toDate | Type version validity – date to, Parameter used to narrow down search results (to a set of issues in types occurring in a given time period) | Calendar | No | |
| isEditable | Whether the field data (of the ParamDefinition object) can be modified | Boolean | No | true or false |
| sourceOfObject | The name of the source from which the field name comes. | String | No | |
| mimeType | Additional information about mimeType. A value supplementing the data about the LOB field, stored in the knownLobMetadata field | String | No | mimeType definitions e.g.: application/json, application/xml, text/html, application/octet-stream, text/plain |
ParamDefinitionPK
| Layers used | Logic |
| Type | Entity |
| complexType | ParamDefinitionPK |
Definition of the primary key of the ParamDefinition entity.
List and meaning of individual fields
| Field | Description | Type | Required | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| definitionName | Unique field name. | String | Yes | |
| version | Field version. | Long | Yes | Value generated automatically after identifying a parameter definition change. |
Control fields and their value definitions for GUI presentation generation mechanisms
Below is a description of enumerators, whose data is included in the ParamDefinition entity description, and on which the rules for building HTML controls during form generation are based.
HtmlSupportedControl
The htmlControlName control field describes a single HTML control associated with a given form field. Below is a list of values that influence the selection of the appropriate GUI form control:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| TEXT | long text, presented in TEXTAREA |
| INTEGER | Integer. Input field with integer format validation |
| CURRENCY | Floating-point number with additional information about the currency (currency code, e.g. PLN, USD, GBP, etc.) |
| NUMBER | Floating-point number. Input field with integer format validation |
| STRING | short text, presented in a regular INPUT TYPE="text" field |
| CHECK | type presented as a CHECKBOX field |
| RADIO | Type presented as a RADIO field |
| DATE | Date type, field with datePicker |
| URL | Text field to which a link can be entered. |
| FILE | Text field to which the location of a local (workstation) file can be entered. |
| SELECT | Single-select drop-down list, but it can be made a multi-select field by setting the appropriate value. |
| MULTI | Multiple-select drop-down list |
| GROUPEDSELECT | Single-select drop-down list, but the list presents grouped name-value pairs |
| GROUPEDMULTI | Drop-down list with multiple selections, but the list displays grouped name-value pairs, but you can make it a multi-select field by setting the appropriate value. |
| LOVSELECT | Drop-down list field with single selection, but the list is displayed in a separate window (LOV - List OF Values) |
| LOVMULTI | Drop-down list field with multiple selections, but the list is displayed in a separate window (LOV - List OF Values), but you can make it a multi-select field by setting the appropriate value. |
| GROUPEDLOVSELECT | Drop-down list field with single selection, but the list is displayed in a separate window (LOV - List OF Values), but the list displays grouped name-value pairs, but you can make it a multi-select field by setting the appropriate value. |
| GROUPEDLOVMULTI | Field with a drop-down list, with the option to select multiple values, but the list is presented in a separate window (LOV - List OF Values), but the list presents grouped name-value pairs |
| SUBFORM | Generation of a GUI subform/dependent case presentation. For the paramType field with the value SUBCASE - see the description AttributeType. |
| SUBTABLE | Generation of lists/tables, for dependent case lists. For the paramType field with the value SUBCASE - see the description AttributeType. |
AttributeType
The attributeType control field defining the types of form fields. It can be the basis for building a value validator. Below is a list of values that affect the construction of the appropriate GUI form control.
| Value | Type name | Java implementation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOOLEAN | Boolean | java.lang.Boolean | List of values corresponding to true and false; |
| BOOLEAN_INTEGER | BooleanInteger | java.lang.Integer | List of values corresponding to true and false with a numeric value; |
| TEXT | Text | java.lang.String | Long text - characters (words, sentences, etc.); |
| STRING | String | java.lang.String | Short text - characters (word, sentence, etc.) |
| PASSWORD | Password | java.lang.String | short text, presented in a regular field with a mask hiding the entered value |
| NUMBER | Number | java.lang.Double | Floating-point number; #########0.#### |
| DECIMAL | Decimal | java.lang.Double | Floating-point number; #########0.#### |
| DOUBLE | Double | java.lang.Double | Floating-point number; #########0.#### |
| FLOAT | Float | java.lang.Float | Floating-point number; ########0.#### |
| CURRENCY | Currency | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.javax.CurrencyValue | Number in currency format, with two decimal places; #########0.## |
| INTEGER | Integer | java.lang.Long | Integer |
| DATE | Date | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.javax.DateInString | Simple date in DD-MM-YYYY format |
| DATE_LONG | DateLong | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.javax.DateInString | Date with time (hour) in DD-MM-YYYY HH24:MI:SS format |
| TIME | Time | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.javax.DateInString | Date with time (hour) in the format DD-MM-YYYY HH24:MI:SS |
| URL | URL | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.javax.URLValue | HTTP address |
| SELECT | n/a | java.util.Collection | Attribute with lists. Multi-valued field. |
| COMPLEX | n/a | java.lang.Object | Complex type, for a field of this type a form will be generated based on data defined in an object meeting the ComplexValue interface. The complex type can also be supported by an HTML control of the SELECT type - then value contains an appropriately prepared form representing the value (based on the implementation of the ComplexValue#encode(Object, String, String) method) |
| LOB | Lob | java.lang.String | Large object |
| SUBCASE | n/a | java.lang.Object | dependent case |
JSONNameValuePair | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.sub.JSONNameValuePairSubType | name and valueobsolete, currently in use is NameValuePair | |
| NVP | NameValuePair | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.sub.NameValuePairSubType | Subtype representing an object with a pair of name and value (with fields name and value) |
| ENTRY | Entry | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.sub.EntrySubType | Subtype representing an Entry object with a pair of key and value (with key and value fields) |
| MAP | Map | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.sub.MapSubType | Subtype representing a list of Entry objects |
| ANY | ANY | pro.ibpm.mercury.attrs.sub.AnySubType | Subtype representing any object |
SourceType
The sourceType control field defining the origin of the dictionary data for the field value. Data source types for GUI form drop-down list controls.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| DEFAULT | Default data origin - for fields of type Integer, Number, Date |
| JSON | A JSON-formatted list in the valueDefinition field of the ParamDefinition entity. |
| WS | The field in the valueDefinition field of the ParamDefinition entity contains the name of the class interpreting the result, and the SOURCE field contains the WebService address using the HTTPS protocol |
| HTTP | The field in the valueDefinition field of the ParamDefinition entity contains an intermediate path to a protected list of elements defined as a file, and the SOURCE field contains a URL directing to a page with the appropriate XML or JSON format - using the HTTP and HTTPS protocols. The page is not secured, or is secured with the BASIC, OAuth mechanism. |
| WEB | In the field valueDefinition of the ParamDefinition entity there is an intermediate path leading to a protected list of elements defined as a file, and in the SOURCE there is a URL directing to a page with the appropriate XML or JSON format - using the HTTP and HTTPS protocols. The server page where the data is located is secured with the FORM mechanism |
| FILE | In the field valueDefinition of the ParamDefinition entity there is an intermediate path leading to a list of elements defined as a file, and in the SOURCE field there is a URL directing to a file with the appropriate XML or JSON format |
| JNDI_RESOURCE | In the field in the valueDefinition field of the ParamDefinition entity there is an intermediate path leading to a list of elements defined as a file, and in the field in the SOURCE field there is a URL directing to a page with the appropriate XML or JSON format - using the HTTP/HTTPS protocol |
| SAVEDVALS | values saved in the database in an array. The array contains rows with fields for the attribute name and the saved value, and its data is completed with the entered, various values from the GUI form. |
| LOCALDAO | using local DAO classes (the DAO class name will be built based on the name of the ParamDefinition parameter) |
| QUERY | SQL query in the valueDefinition field of the ParamDefinition entity. The JNDI data source should be in the sourceJndiName field or the JDBC URL in the source field |
Footnotes
-
Teaser - a short description of the case, which is used to present the case in the search results. ↩
-
A list of available HTML event names can be found at https://www.w3schools.com/tags/ref_eventattributes.asp. ↩